Lower Heating and Cooling Costs
Insulation and Air Leak Sealing
Sealing air leaks and insulating the “envelope” of your home — including outer walls, ceiling, windows, doors, and floors — is one of the most cost-effective ways to improve energy efficiency and comfort. You can save up to 10-20% on your heating and cooling costs.
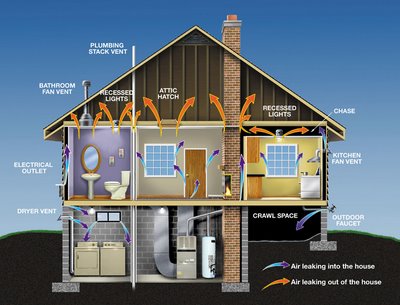
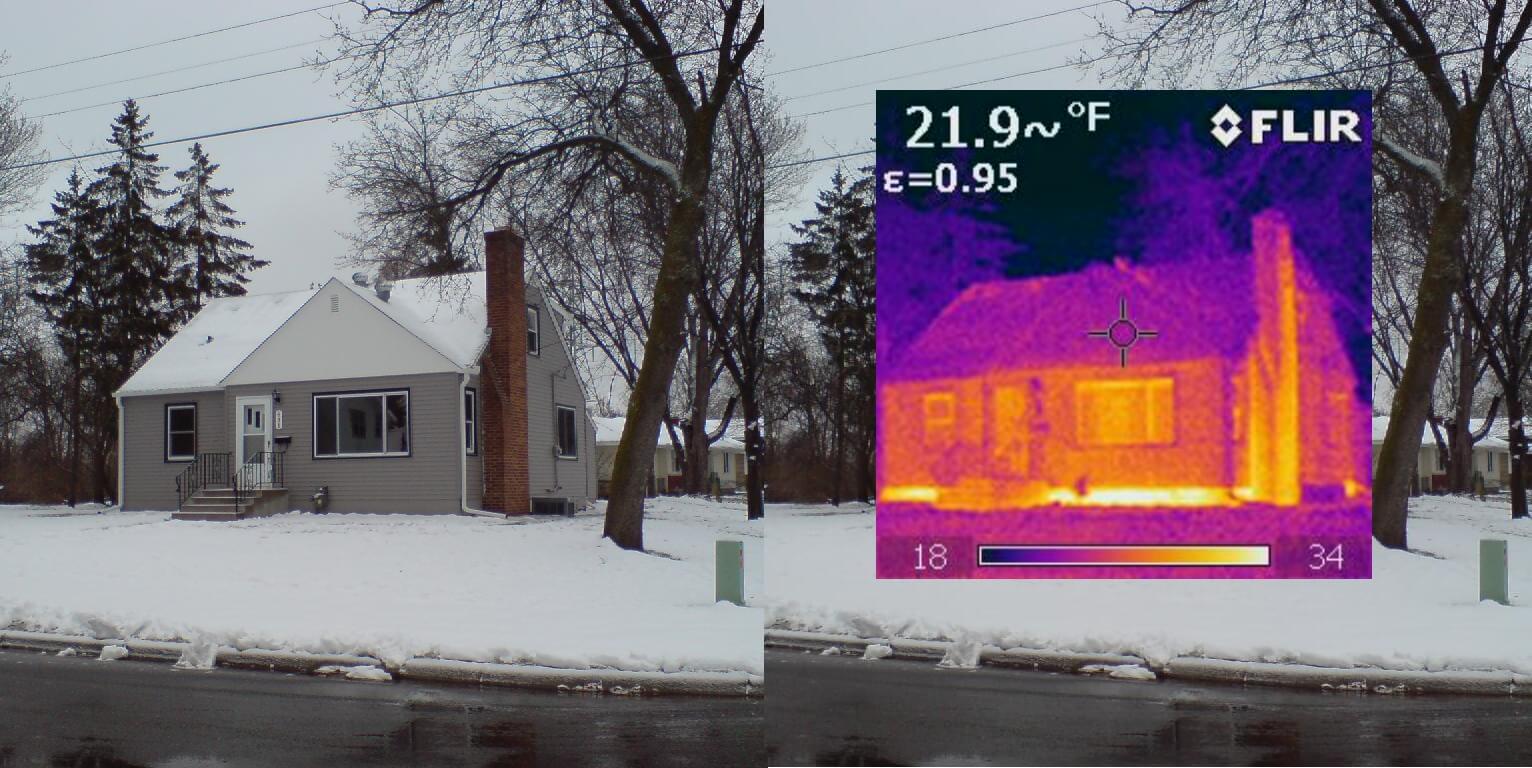
Attic insulation and air leaks are often the biggest contributors to heat loss in a home.

Save Energy by Sealing Leaks First
Sealing air leaks throughout your home is essential to reduce heat loss and stop drafts. Adding insulation will further help block heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, leading to significant savings on heating and cooling costs.
Insulation performs best when air isn’t moving through or around it. For optimal results, it’s crucial to seal air leaks before installing insulation. This ensures the insulation works at its full potential.
Common Sources of Air Leaks
Many air leaks and drafts are easy to spot because you can feel them, such as those around windows and doors. However, hidden gaps in attics, basements, and crawlspaces can be bigger problems. Sealing these leaks with caulk, spray foam, or weather stripping will significantly improve your home’s comfort and help lower your utility bills.
Will Sealing My Home Too Tightly Be a Problem?
Homeowners sometimes worry about sealing their home too tightly. However, this is generally not a concern, especially in older homes. Adequate fresh air is necessary for good indoor air quality, and there are specific guidelines that ensure enough ventilation is maintained.
After completing any sealing project, it’s a good idea to have a heating and cooling technician check that your combustion appliances (such as gas or oil-fired furnaces, water heaters, and dryers) are venting properly.
Adding Insulation
Insulation helps maintain a comfortable temperature in your home, keeping it warm in winter and cool in summer. There are several common types of insulation, including fiberglass (in both batt and blown forms), cellulose, rigid foam board, and spray foam.
When installed correctly, and paired with proper air sealing, any type of insulation can improve comfort and lower energy bills throughout the year.
Understanding Insulation Performance
Insulation effectiveness is measured by its R-value — its ability to resist heat flow. The higher the R-value, the greater the insulating power. The recommended R-value varies for different areas of your home, such as walls, attics, basements, and crawlspaces, and also depends on the climate in your region.
To get the best results and save the most energy, the attic is often the easiest place to add insulation. A simple way to check if you need more insulation is to look at the floor of your attic. If the insulation is level with or below the attic floor joists, it’s likely time to add more.
Attic Insulation Recommendations
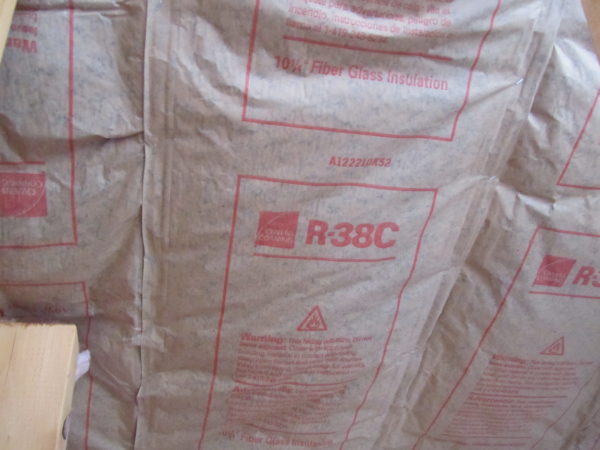
For most attics, the recommended insulation level is R-38 (about 12–15 inches of insulation, depending on the type). In colder climates, R-49 may be recommended for optimal energy savings. Often times closed Cell spray Foam is the best option to achieve the highest r-value.
Don’t forget to check your basement insulation as well — adding insulation here can also have a significant impact on your home’s energy efficiency.