Recycling Asphalt Roof Shingles
Recycling Roof Shingles
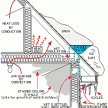
Lifespan of Asphalt Roof Shingles
Asphalt Roof Shingles and Landfills
Millions of tons of roofing materials are sent to the landfill each year. A common roadblock for many contractors to increasing recycling efforts is a lack of recycling programs and technical reuse limitations.
Owens Corning Recycling of Asphalt Roof Shingles
Recognizing the opportunity to provide a more sustainable end-of-life solution for asphalt shingles, Owens Corning’s Roofing business has done a nice job developing an innovative program to simplify shingle recycling for their preferred roofing contractors.
Through the program, Owens Corning connects roofing contractors with convenient drop-offs and recycling centers run by Heritage Environmental Services. Heritage, the largest privately-held environmental services company in the US, will provide dedicated, convenient drop-off centers that will recycle and process shingle tear-offs for the materials to be used in paving.
Owens Corning is taking a proactive step toward removing barriers to keeping recyclable waste from going to landfills. Although they only offer this program to their “preferred contractors” it’s still a start in the right direction.
The shingles contain 40 percent asphalt, according to the Construction Materials Recycling Association (CMRA) making it an attractive substitute for virgin asphalt. The National Asphalt Paving Association estimates that using 5 percent recycled shingle byproduct can save between $1 and $2.80 per ton of hot-mix asphalt.
Alternatives to Disposal
Some attempts have been made to recycle shingles into new shingles, but problems persist in reprocessing shingles to conform to feedstock requirements.
Recycling involves the use of heavy equipment (tailored for processing shingles and minimizing dust) to grind or shred shingle waste to a size useful in paving materials:
- Parking lots or temporary roadways
- Aggregate base course
- Hot mix asphalt wear course
- Pothole/road patch material
- Granular base stabilization layer
- Expansion joints
- Moisture barrier under base course